EMC VNX driver consists of EMCCLIISCSIDriver
and EMCCLIFCDriver, and supports both iSCSI and FC protocol.
EMCCLIISCSIDriver (VNX iSCSI driver) and
EMCCLIFCDriver (VNX FC driver) are separately
based on the ISCSIDriver and FCDriver
defined in Block Storage.
The VNX iSCSI driver and VNX FC driver perform the volume operations by executing Navisphere CLI (NaviSecCLI) which is a command line interface used for management, diagnostics, and reporting functions for VNX.
VNX Operational Environment for Block version 5.32 or higher.
VNX Snapshot and Thin Provisioning license should be activated for VNX.
Navisphere CLI v7.32 or higher is installed along with the driver.
Create, delete, attach, and detach volumes.
Create, list, and delete volume snapshots.
Create a volume from a snapshot.
Copy an image to a volume.
Clone a volume.
Extend a volume.
Migrate a volume.
Retype a volume.
Get volume statistics.
Create and delete consistency groups.
Create, list, and delete consistency group snapshots.
Modify consistency groups.
Efficient non-disruptive volume backup.
This section contains instructions to prepare the Block Storage nodes to use the EMC VNX driver. You install the Navisphere CLI, install the driver, ensure you have correct zoning configurations, and register the driver.
Navisphere CLI needs to be installed on all Block Storage nodes within an OpenStack deployment. You need to download different versions for different platforms.
For Ubuntu x64, DEB is available at EMC OpenStack Github.
For all other variants of Linux, Navisphere CLI is available at Downloads for VNX2 Series or Downloads for VNX1 Series.
After installation, set the security level of Navisphere CLI to low:
$ /opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli security -certificate -setLevel low
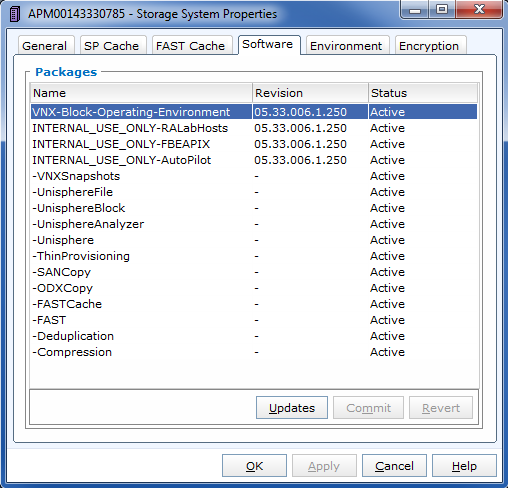
Make sure your have following software installed for certain features.
| Feature | Software Required |
All |
ThinProvisioning |
All |
VNXSnapshots |
FAST cache support |
FASTCache |
Create volume with type |
Compression |
Create volume with type |
Deduplication |
You can check the status of your array software in the "Software" page of "Storage System Properties". Here is how it looks like.
Both EMCCLIISCSIDriver and
EMCCLIFCDriver are included in the Block Storage
installer package:
emc_vnx_cli.pyemc_cli_fc.py(forEMCCLIFCDriver)emc_cli_iscsi.py(forEMCCLIISCSIDriver)
For FC Driver, FC zoning is properly configured between hosts and VNX. Check the section called “Register FC port with VNX” for reference.
For iSCSI Driver, make sure your VNX iSCSI port is accessible by your hosts. Check the section called “Register iSCSI port with VNX” for reference.
You can use initiator_auto_registration=True
configuration to avoid register the ports manually. Please check
the detail of the configuration in
the section called “Backend configuration” for reference.
If you are trying to setup multipath, please refer to Multipath Setup in the section called “Multipath setup”.
Make the following changes in
/etc/cinder/cinder.conf file:
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Changes to your configuration won't take effect until your restart your cinder service. |
Here is a sample of minimum backend configuration. See following
sections for the detail of each option Replace
EMCCLIFCDriver to
EMCCLIISCSIDriver if your are using the iSCSI
driver.
[DEFAULT] enabled_backends = vnx_array1 [vnx_array1] san_ip = 10.10.72.41 san_login = sysadmin san_password = sysadmin naviseccli_path = /opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli volume_driver=cinder.volume.drivers.emc.emc_cli_fc.EMCCLIFCDriver initiator_auto_registration=True
Here is a sample of a multi-backend configuration. See following
sections for the detail of each option. Replace
EMCCLIFCDriver to
EMCCLIISCSIDriver if your are using the iSCSI
driver.
[DEFAULT] enabled_backends=backendA, backendB [backendA] storage_vnx_pool_names = Pool_01_SAS, Pool_02_FLASH san_ip = 10.10.72.41 storage_vnx_security_file_dir = /etc/secfile/array1 naviseccli_path = /opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli volume_driver=cinder.volume.drivers.emc.emc_cli_fc.EMCCLIFCDriver initiator_auto_registration=True [backendB] storage_vnx_pool_names = Pool_02_SAS san_ip = 10.10.26.101 san_login = username san_password = password naviseccli_path = /opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli volume_driver=cinder.volume.drivers.emc.emc_cli_fc.EMCCLIFCDriver initiator_auto_registration=True
For more details on multi-backends, see OpenStack Cloud Administration Guide
Specify the SP A and SP B IP to connect.
san_ip = <IP of VNX Storage Processor A> san_secondary_ip = <IP of VNX Storage Processor B>
There are two ways to specify the credentials.
Use plain text username and password.
Supply for plain username and password as below.
san_login = <VNX account with administrator role> san_password = <password for VNX account> storage_vnx_authentication_type = global
Valid values for
storage_vnx_authentication_type are:
global (default), local,
ldap
Use Security file
This approach avoids the plain text password in your cinder configuration file. Supply a security file as below:
storage_vnx_security_file_dir=<path to security file>
Please check Unisphere CLI user guide or the section called “Authenticate by security file” for how to create a security file.
Specify the absolute path to your naviseccli.
naviseccli_path = /opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli
- VNX pool names
- Initiator auto registration
- Force delete volumes in storage group
- Over subscription in thin provisioning
- Storage group automatic deletion
- Initiator auto deregistration
- FC SAN auto zoning
- Volume number threshold
- iSCSI initiators
- Default timeout
- Max LUNs per storage group
- Ignore pool full threshold
Specify the list of pools to be managed, separated by ','. They should already exist in VNX.
storage_vnx_pool_names = pool 1, pool 2
If this value is not specified, all pools of the array will be used.
When initiator_auto_registration=True, the
driver will automatically register initiators to all working
target ports of the VNX array during volume attaching (The
driver will skip those initiators that have already been
registered) if the option io_port_list is not
specified in cinder.conf.
If the user wants to register the initiators with some specific ports but not register with the other ports, this functionality should be disabled.
When a comma-separated list is given to
io_port_list, the driver will only register the
initiator to the ports specified in the list and only return
target port(s) which belong to the target ports in the
io_port_list instead of all target ports.
Example for FC ports:
io_port_list=a-1,B-3
aorBis Storage Processor, number1and3are Port ID.Example for iSCSI ports:
io_port_list=a-1-0,B-3-0
aorBis Storage Processor, the first numbers1and3are Port ID and the second number0is Virtual Port ID
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
Some available volumes may remain in storage
group on the VNX array due to some OpenStack timeout issue. But
the VNX array do not allow the user to delete the volumes which
are in storage group. Option
force_delete_lun_in_storagegroup is
introduced to allow the user to delete the
available volumes in this tricky situation.
When force_delete_lun_in_storagegroup=True in
the back-end section, the driver will move the volumes out of
storage groups and then delete them if the user tries to delete
the volumes that remain in storage group on the VNX array.
The default value of
force_delete_lun_in_storagegroup is
False.
Over subscription allows that the sum of all volumes' capacity (provisioned capacity) to be larger than the pool's total capacity.
max_over_subscription_ratio in the back-end
section is the ratio of provisioned capacity over total
capacity.
The default value of
max_over_subscription_ratio is 20.0, which
means the provisioned capacity can not exceed the total
capacity. If the value of this ratio is set larger than 1.0, the
provisioned capacity can exceed the total capacity.
For volume attaching, the driver has a storage group on VNX for
each compute node hosting the vm instances which are going to
consume VNX Block Storage (using compute node's hostname as
storage group's name). All the volumes attached to the VM
instances in a compute node will be put into the storage group.
If destroy_empty_storage_group=True, the
driver will remove the empty storage group after its last volume
is detached. For data safety, it does not suggest to set
destroy_empty_storage_group=True unless the
VNX is exclusively managed by one Block Storage node because
consistent lock_path is required for operation synchronization
for this behavior.
Enabling storage group automatic deletion is the precondition of
this function. If
initiator_auto_deregistration=True is set,
the driver will deregister all the initiators of the host after
its storage group is deleted.
The EMC VNX FC driver supports FC SAN auto zoning when ZoneManager
is configured. Set zoning_mode to
fabric in DEFAULT section
to enable this feature. For ZoneManager configuration, please
refer to Block Storage official guide.
In VNX, there is a limitation on the number of pool volumes that can be created in the system. When the limitation is reached, no more pool volumes can be created even if there is remaining capacity in the storage pool. In other words, if the scheduler dispatches a volume creation request to a back end that has free capacity but reaches the volume limitation, the creation fails.
The default value of
check_max_pool_luns_threshold is
False. When
check_max_pool_luns_threshold=True, the
pool-based back end will check the limit and will report 0 free
capacity to the scheduler if the limit is reached. So the scheduler
will be able to skip this kind of pool-based back end that runs out
of the pool volume number.
iscsi_initiators is a dictionary of IP
addresses of the iSCSI initiator ports on OpenStack Nova/Cinder
nodes which want to connect to VNX via iSCSI. If this option is
configured, the driver will leverage this information to find an
accessible iSCSI target portal for the initiator when attaching
volume. Otherwise, the iSCSI target portal will be chosen in a
relative random way.
This option is only valid for iSCSI driver.
Here is an example. VNX will connect host1
with 10.0.0.1 and
10.0.0.2. And it will connect
host2 with 10.0.0.3.
The key name (like host1 in the example)
should be the output of command hostname.
iscsi_initiators = {"host1":["10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.2"],"host2":["10.0.0.3"]}
Specify the timeout(minutes) for operations like LUN migration, LUN creation, etc. For example, LUN migration is a typical long running operation, which depends on the LUN size and the load of the array. An upper bound in the specific deployment can be set to avoid unnecessary long wait.
The default value for this option is infinite.
Example:
default_timeout = 10
max_luns_per_storage_group specify the max
number of LUNs in a storage group. Default value is 255. It is
also the max value supportedby VNX.
Extra specs are used in volume types created in cinder as the preferred property of the volume.
The Block storage scheduler will use extra specs to find the suitable back end for the volume and the Block storage driver will create the volume based on the properties specified by the extra spec.
Use following command to create a volume type:
$ cinder type-create "demoVolumeType"
Use following command to update the extra spec of a volume type:
$ cinder type-key "demoVolumeType" set provisioning:type=thin
Volume types can also be configured in OpenStack Horizon.
In VNX Driver, we defined several extra specs. They are introduced below:
Key:
provisioning:typePossible Values:
thick
Volume is fully provisioned.
Example 2.9. creating a
thickvolume type:$ cinder type-create "ThickVolumeType" $ cinder type-key "ThickVolumeType" set provisioning:type=thick thick_provisioning_support='<is> True'
thin
Volume is virtually provisioned
Example 2.10. creating a
thinvolume type:$ cinder type-create "ThinVolumeType" $ cinder type-key "ThinVolumeType" set provisioning:type=thin thin_provisioning_support='<is> True'
deduplicated
Volume is
thinand deduplication is enabled. The administrator shall go to VNX to configure the system level deduplication settings. To create a deduplicated volume, the VNX Deduplication license must be activated on VNX, and specifydeduplication_support=Trueto let Block Storage scheduler find the proper volume back end.Example 2.11. creating a
deduplicatedvolume type:$ cinder type-create "DeduplicatedVolumeType" $ cinder type-key "DeduplicatedVolumeType" set provisioning:type=deduplicated deduplication_support='<is> True'
compressed
Volume is
thinand compression is enabled. The administrator shall go to the VNX to configure the system level compression settings. To create a compressed volume, the VNX Compression license must be activated on VNX , and usecompression_support=Trueto let Block Storage scheduler find a volume back end. VNX does not support creating snapshots on a compressed volume.Example 2.12. creating a
compressedvolume type:$ cinder type-create "CompressedVolumeType" $ cinder type-key "CompressedVolumeType" set provisioning:type=compressed compression_support='<is> True'
Default:
thick
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
Key:
storagetype:tieringPossible Values:
StartHighThenAutoAutoHighestAvailableLowestAvailableNoMovement
Default:
StartHighThenAuto
VNX supports fully automated storage tiering which requires the
FAST license activated on the VNX. The OpenStack administrator can
use the extra spec key storagetype:tiering to
set the tiering policy of a volume and use the key
fast_support='<is> True' to let Block
Storage scheduler find a volume back end which manages a VNX with
FAST license activated. Here are the five supported values for the
extra spec key storagetype:tiering:
Example 2.13. creating a volume types with tiering policy:
$ cinder type-create "ThinVolumeOnLowestAvaibleTier" $ cinder type-key "CompressedVolumeOnLowestAvaibleTier" set provisioning:type=thin storagetype:tiering=Auto fast_support='<is> True'
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Tiering policy can not be applied to a deduplicated volume. Tiering policy of the deduplicated LUN align with the settings of the pool. |
Key:
fast_cache_enabledPossible Values:
TrueFalse
Default:
False
VNX has FAST Cache feature which requires the FAST Cache license
activated on the VNX. Volume will be created on the backend with
FAST cache enabled when True is specified.
Key:
copytype:snapPossible Values:
TrueFalse
Default:
False
The VNX driver supports snap-copy, which extremely accelerates the process for creating a copied volume.
By default, the driver will do full data copy when creating a volume from a snapshot or cloning a volume, which is time-consuming especially for large volumes. When the snap-copy is used, the driver will simply create a snapshot and mount it as a volume for the 2 kinds of operations which will be instant even for large volumes.
To enable this functionality, the source volume should have
copytype:snap=True in the extra specs of its
volume type. Then the new volume cloned from the source or copied
from the snapshot for the source, will be in fact a snap-copy
instead of a full copy. If a full copy is needed, retype/migration
can be used to convert the snap-copy volume to a full-copy volume
which may be time-consuming.
$ cinder type-create "SnapCopy" $ cinder type-key "SnapCopy" set copytype:snap=True
User can determine whether the volume is a snap-copy volume or not by showing its metadata. If the 'lun_type' in metadata is 'smp', the volume is a snap-copy volume. Otherwise, it is a full-copy volume.
$ cinder metadata-show <volume>
Constraints:
copytype:snap=Trueis not allowed in the volume type of a consistency group.Clone and snapshot creation are not allowed on a copied volume created through the snap-copy before it is converted to a full copy.
The number of snap-copy volume created from a source volume is limited to 255 at one point in time.
The source volume which has snap-copy volume can not be deleted.
Key:
pool_namePossible Values: name of the storage pool managed by cinder
Default: None
If the user wants to create a volume on a certain storage pool in a backend that manages multiple pools, a volume type with a extra spec specified storage pool should be created first, then the user can use this volume type to create the volume.
Example 2.14. Creating the volume type:
$ cinder type-create "HighPerf" $ cinder type-key "HighPerf" set pool_name=Pool_02_SASFLASH volume_backend_name=vnx_41
OpenStack supports read-only volumes. The following command can be used to set a volume as read-only.
$ cinder readonly-mode-update <volume> True
After a volume is marked as read-only, the driver will forward the information when a hypervisor is attaching the volume and the hypervisor will make sure the volume is read-only.
The default implementation in Cinder for non-disruptive volume backup is not efficient since a cloned volume will be created during backup.
The approach of efficient backup is to create a snapshot for the volume and connect this snapshot (a mount point in VNX) to the Cinder host for volume backup. This eliminates migration time involved in volume clone.
Constraints:
Backup creation for a snap-copy volume is not allowed if the volume status is
in-usesince snapshot cannot be taken from this volume.
Enabling multipath volume access is recommended for robust data access. The major configuration includes:
Install
multipath-tools,sysfsutilsandsg3-utilson nodes hosting Nova-Compute and Cinder-Volume services (Please check the operating system manual for the system distribution for specific installation steps. For Red Hat based distributions, they should bedevice-mapper-multipath,sysfsutilsandsg3_utils).Specify
use_multipath_for_image_xfer=truein cinder.conf for each FC/iSCSI back end.Specify
iscsi_use_multipath=Trueinlibvirtsection ofnova.conf. This option is valid for both iSCSI and FC driver.
For multipath-tools, here is an EMC recommended sample of
/etc/multipath.conf.
user_friendly_names is not specified in the
configuration and thus it will take the default value
no. It is NOT recommended to set it to
yes because it may fail operations such as VM
live migration.
blacklist {
# Skip the files under /dev that are definitely not FC/iSCSI devices
# Different system may need different customization
devnode "^(ram|raw|loop|fd|md|dm-|sr|scd|st)[0-9]*"
devnode "^hd[a-z][0-9]*"
devnode "^cciss!c[0-9]d[0-9]*[p[0-9]*]"
# Skip LUNZ device from VNX
device {
vendor "DGC"
product "LUNZ"
}
}
defaults {
user_friendly_names no
flush_on_last_del yes
}
devices {
# Device attributed for EMC CLARiiON and VNX series ALUA
device {
vendor "DGC"
product ".*"
product_blacklist "LUNZ"
path_grouping_policy group_by_prio
path_selector "round-robin 0"
path_checker emc_clariion
features "1 queue_if_no_path"
hardware_handler "1 alua"
prio alua
failback immediate
}
}
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
When multipath is used in OpenStack, multipath faulty devices may come out in Nova-Compute nodes due to different issues (Bug 1336683 is a typical example). |
A solution to completely avoid faulty devices has not been found
yet. faulty_device_cleanup.py mitigates this
issue when VNX iSCSI storage is used. Cloud administrators can
deploy the script in all Nova-Compute nodes and use a CRON job to
run the script on each Nova-Compute node periodically so that
faulty devices will not stay too long. Please refer to:
VNX faulty device cleanup for detailed usage and the script.
EMC VNX iSCSI driver caches the iSCSI ports information, so that
the user should restart the cinder-volume service or wait for
seconds (which is configured by
periodic_interval in
cinder.conf) before any volume attachment
operation after changing the iSCSI port configurations. Otherwise
the attachment may fail because the old iSCSI port configurations
were used.
VNX does not support extending the thick volume which has a
snapshot. If the user tries to extend a volume which has a
snapshot, the status of the volume would change to
error_extending.
It is not recommended to deploy the driver on a compute node if
cinder upload-to-image --force True is used
against an in-use volume. Otherwise,
cinder upload-to-image --force True will
terminate the data access of the vm instance to the volume.
When the driver notices that there is no existing storage group that has the host name as the storage group name, it will create the storage group and also add the compute node's or Block Storage nodes' registered initiators into the storage group.
If the driver notices that the storage group already exists, it will assume that the registered initiators have also been put into it and skip the operations above for better performance.
It is recommended that the storage administrator does not create the storage group manually and instead relies on the driver for the preparation. If the storage administrator needs to create the storage group manually for some special requirements, the correct registered initiators should be put into the storage group as well (otherwise the following volume attaching operations will fail ).
EMC VNX driver supports storage-assisted volume migration, when
the user starts migrating with
cinder migrate --force-host-copy False <volume_id> <host>
or
cinder migrate <volume_id> <host>,
cinder will try to leverage the VNX's native volume migration
functionality.
In following scenarios, VNX storage-assisted volume migration will not be triggered:
Volume migration between back ends with different storage protocol, ex, FC and iSCSI.
Volume is to be migrated across arrays.
VNX credentials are necessary when the driver connects to the VNX system. Credentials in global, local and ldap scopes are supported. There are two approaches to provide the credentials:
The recommended one is using the Navisphere CLI security file to provide the credentials which can get rid of providing the plain text credentials in the configuration file. Following is the instruction on how to do this.
Find out the Linux user id of the
cinder-volumeprocesses. Assuming the servicecinder-volumeis running by the accountcinder.Run
suas root user.In
/etc/passwd, changecinder:x:113:120::/var/lib/cinder:/bin/falsetocinder:x:113:120::/var/lib/cinder:/bin/bash(This temporary change is to make step 4 work.)Save the credentials on behave of
cinderuser to a security file (assuming the array credentials areadmin/admininglobalscope). In the command below, the '-secfilepath' switch is used to specify the location to save the security file.# su -l cinder -c '/opt/Navisphere/bin/naviseccli -AddUserSecurity -user admin -password admin -scope 0 -secfilepath <location>'
Change
cinder:x:113:120::/var/lib/cinder:/bin/bashback tocinder:x:113:120::/var/lib/cinder:/bin/falsein/etc/passwdRemove the credentials options
san_login,san_passwordandstorage_vnx_authentication_typefrom cinder.conf. (normally it is/etc/cinder/cinder.conf). Add optionstorage_vnx_security_file_dirand set its value to the directory path of your security file generated in step 4. Omit this option if-secfilepathis not used in step 4.Restart the
cinder-volumeservice to validate the change.
This configuration is only required when
initiator_auto_registration=False.
To access VNX storage, the compute nodes should be registered on VNX first if initiator auto registration is not enabled.
To perform "Copy Image to Volume" and "Copy Volume
to Image" operations, the nodes running the
cinder-volume
service (Block Storage nodes) must be registered with the VNX as
well.
The steps mentioned below are for the compute nodes. Please follow the same steps for the Block Storage nodes also (The steps can be skipped if initiator auto registration is enabled).
Assume
20:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2:21:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2is the WWN of a FC initiator port name of the compute node whose hostname and IP aremyhost1and10.10.61.1. Register20:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2:21:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2in Unisphere:Login to Unisphere, go to .
Refresh and wait until the initiator
20:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2:21:00:00:24:FF:48:BA:C2with SP PortA-1appears.Click the button, select CLARiiON/VNX and enter the hostname (which is the output of the linux command
hostname) and IP address:Hostname :
myhost1IP :
10.10.61.1Click
Then host
10.10.61.1will appear under as well.
Register the wwn with more ports if needed.
This configuration is only required when
initiator_auto_registration=False.
To access VNX storage, the compute nodes should be registered on VNX first if initiator auto registration is not enabled.
To perform "Copy Image to Volume" and "Copy Volume to Image" operations, the nodes running the cinder-volume service (Block Storage nodes) must be registered with the VNX as well.
The steps mentioned below are for the compute nodes. Please follow the same steps for the Block Storage nodes also (The steps can be skipped if initiator auto registration is enabled).
On the compute node with IP address
10.10.61.1and hostnamemyhost1, execute the following commands (assuming10.10.61.35is the iSCSI target):Start the iSCSI initiator service on the node
# /etc/init.d/open-iscsi start
Discover the iSCSI target portals on VNX
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p 10.10.61.35
Enter
/etc/iscsi# cd /etc/iscsi
Find out the iqn of the node
# more initiatorname.iscsi
Login to VNX from the compute node using the target corresponding to the SPA port:
# iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.apm01234567890.a0 -p 10.10.61.35 -l
Assume
iqn.1993-08.org.debian:01:1a2b3c4d5f6gis the initiator name of the compute node. Registeriqn.1993-08.org.debian:01:1a2b3c4d5f6gin Unisphere:Login to Unisphere, go to .
Refresh and wait until the initiator
iqn.1993-08.org.debian:01:1a2b3c4d5f6gwith SP PortA-8v0appears.Click the button, select CLARiiON/VNX and enter the hostname (which is the output of the linux command
hostname) and IP address:Hostname :
myhost1IP :
10.10.61.1Click
Then host
10.10.61.1will appear under as well.
Logout iSCSI on the node:
# iscsiadm -m node -u
Login to VNX from the compute node using the target corresponding to the SPB port:
# iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.apm01234567890.b8 -p 10.10.61.36 -l
In Unisphere register the initiator with the SPB port.
Logout iSCSI on the node:
# iscsiadm -m node -u
Register the iqn with more ports if needed.