Resource Monitoring¶
Blazar monitors states of resources and heals reservations which are expected to suffer from resource failure. Resource specific functionality, e.g., calling Nova APIs, is provided as a monitoring plugin. The following sections describe the resource monitoring feature in detail.
Monitoring Type¶
Blazar supports 2 types of monitoring - push-based and polling-based.
Push-based monitoring
The monitor listens to notification messages sent by other components, e.g., sent by Nova for the host monitoring plugin. And it picks up messages which refer to the resources managed by Blazar. Event types, topics to subscribe and notification callbacks are provided by monitoring plugins.
Polling-based monitoring
The blazar-manager periodically calls a states check method of monitoring plugins. Then, the monitoring plugins check states of resources, e.g., List Hypervisors of the Compute API is used for the host monitoring plugin.
Admins can enable/disable these monitoring by setting configuration options.
Healing¶
When the monitor detects a resource failure, it heals reservations which are expected to suffer from the failure. Note that it does not immediately heal all of reservations for the failed resource because the resource is expected to recover sometime in the future, i.e., the monitor heals only reservations which are active or will start soon.
In addition, the monitor periodically checks validity of reservations and heals invalid reservations. Therefore, even though the failed resource did not recover in the last interval, the periodic task heals invalid reservations which will start in the next interval.
The healing flow is as follows:
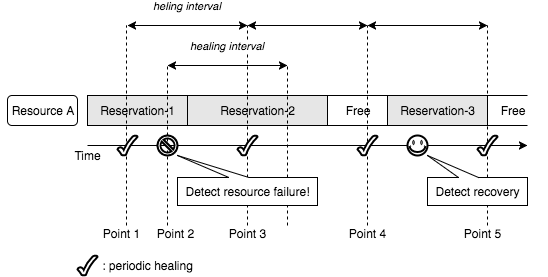
- Resource A is reserved for the Reservation-1, Reservation-2 and Reservation-3 as shown in the following diagram.
- At the point 1, the periodic task in the manager checks if there is any reservation to heal and it detects there is not.
- At the point 2, the manager detects a failure of the resource A. Then, it heals active reservations and reservations which will start in the healing interval. In this case, Reservation-1 and Reservation-2 are healed immediately.
- At the point 3, the periodic task checks if there is any reservation to heal. In this case, the task finds out there is no reservation to heal because the resource has not yet recovered but no reservation will start in next interval. Reservation-2 has been already healed in step 3.
- At the point 4, the periodic task checks if there is any reservation to heal again. In this case, the task finds out Reservation-3 needs to be healed because it will start in the next interval and the resource has not yet recovered.
- Before the point 5, the manager detects a recovery of the resource.
- At the point 5, the periodic task finds out there is no failed resource and nothing to do.
Flags¶
Leases and reservations have flags that indicate states of reserved resources. Reservations have the following two flags:
- missing_resources: If any resource allocated to the reservation fails and no alternative resource found, this flag is set True.
- resources_changed: If any resource allocated to the active reservation and alternative resource is reallocated, this flag is set True.
Leases have the following flag:
- degraded: If the missing_resources or the resources_changed flags of any reservation included in the lease is True, then it is True.
Lease owners can see health of the lease and reservations included in the lease by checking these flags.
Monitoring Resources¶
Resource specific functionality is provided as a monitoring plugin. The following resource is currently supported.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.